"Delivering reliable seismic hazard solutions worldwide" ⚡
1️⃣ PSHA Background
Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Assessment (PSHA) is the standard for modern seismic hazard analysis, replacing older deterministic methods. Its main advantage: it incorporates randomness in earthquake magnitude, frequency, and location—known as aleatory variability.
PSHA relies on two main models:
-
Seismic Source Characterization (SSC): identifies where earthquakes may occur, their frequency, and maximum magnitudes.
-
Ground Motion Prediction (GM): predicts physical earthquake parameters, such as spectral acceleration and peak ground acceleration (PGA).
By considering all possible earthquake scenarios, PSHA produces seismic hazard curves, showing the probability of exceeding certain ground motion levels over time.
Epistemic uncertainty (modeling uncertainty) is handled via logic trees, where alternative models are weighted based on expert judgment.
2️⃣ Geological, Geophysical, and Geotechnical Database 🌍
For reliable site-specific PSHA:
-
Regional, near-regional, and site-specific investigations are conducted.
-
Data includes seismic reflection surveys, borehole geophysics, and microgravity studies.
-
All information is integrated into GIS for comparison and visualization.
Purpose: understand geodynamics, tectonic regime, and potential geological hazards affecting the site.
3️⃣ Seismological Database 📊
A comprehensive earthquake catalogue is compiled, including historical and instrumentally recorded events.
-
Helps create magnitude-frequency distributions for seismic sources.
-
Visualized in GIS maps to compare seismic sources with actual earthquake data.
Completeness analysis ensures even smaller events are accounted for in the hazard assessment.
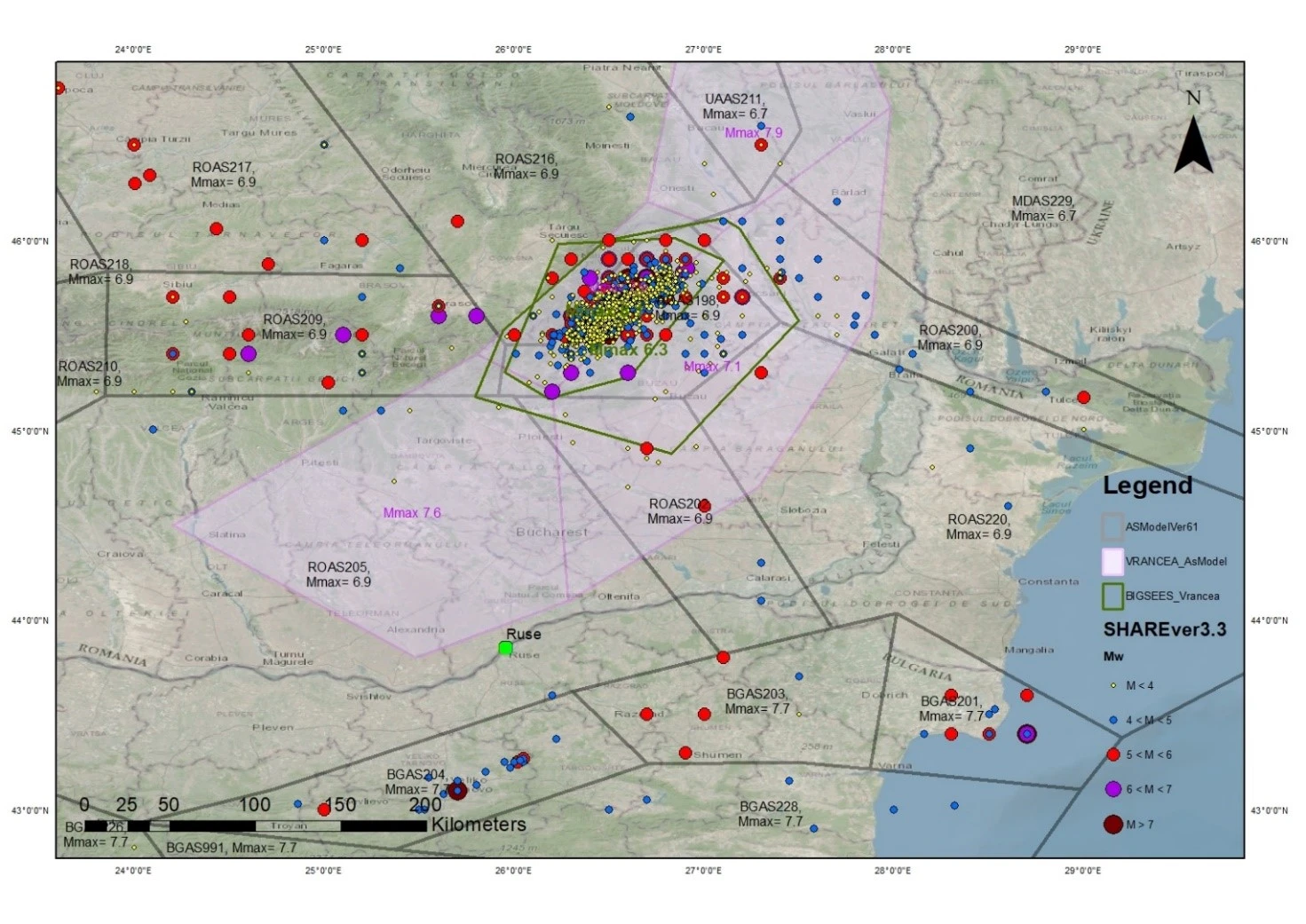
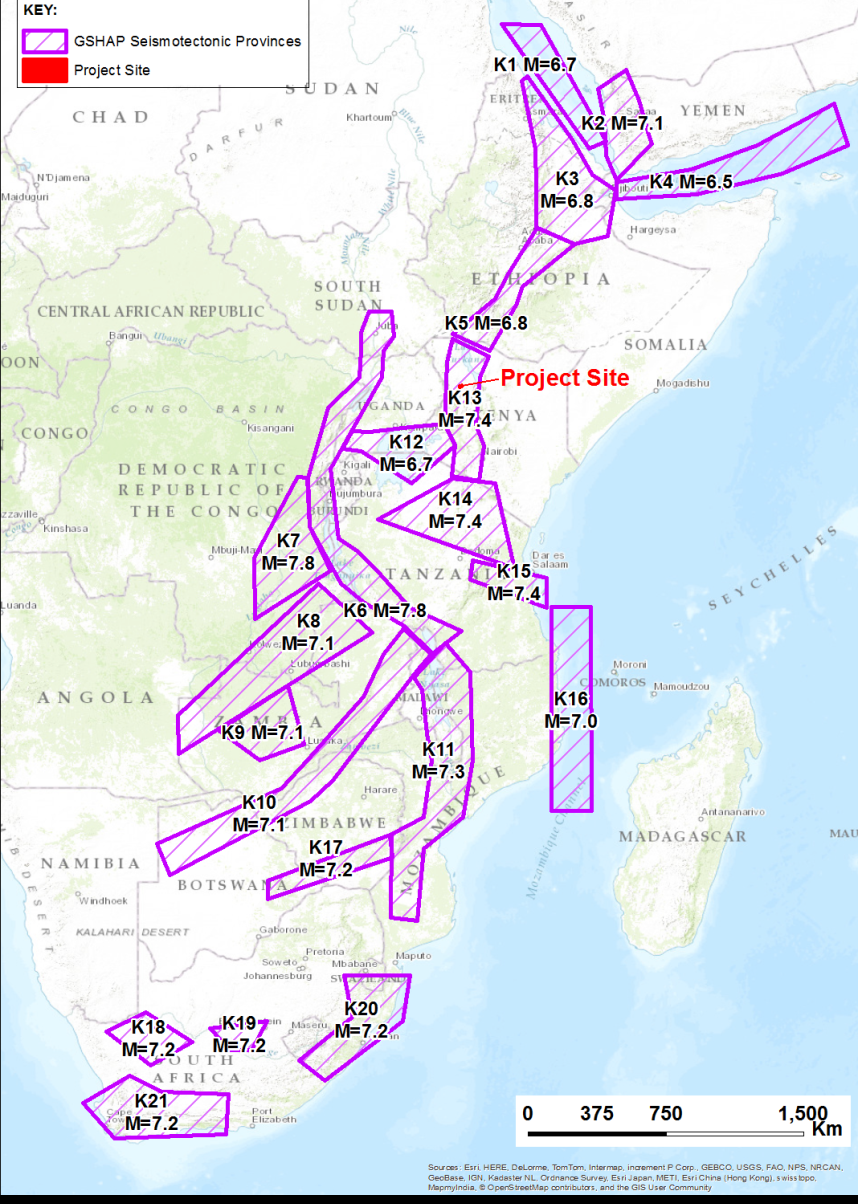
4️⃣ Seismic Source Characterization Model
Seismotectonic modeling links geological, geophysical, geotechnical, and seismological data to define seismic sources:
-
Areal sources: for unknown fault locations.
-
Fault sources: known faults, modeled with multi-planar features.
-
Point sources: distributed seismicity.
All credible models are considered in PSHA with appropriate weights to capture epistemic uncertainty.
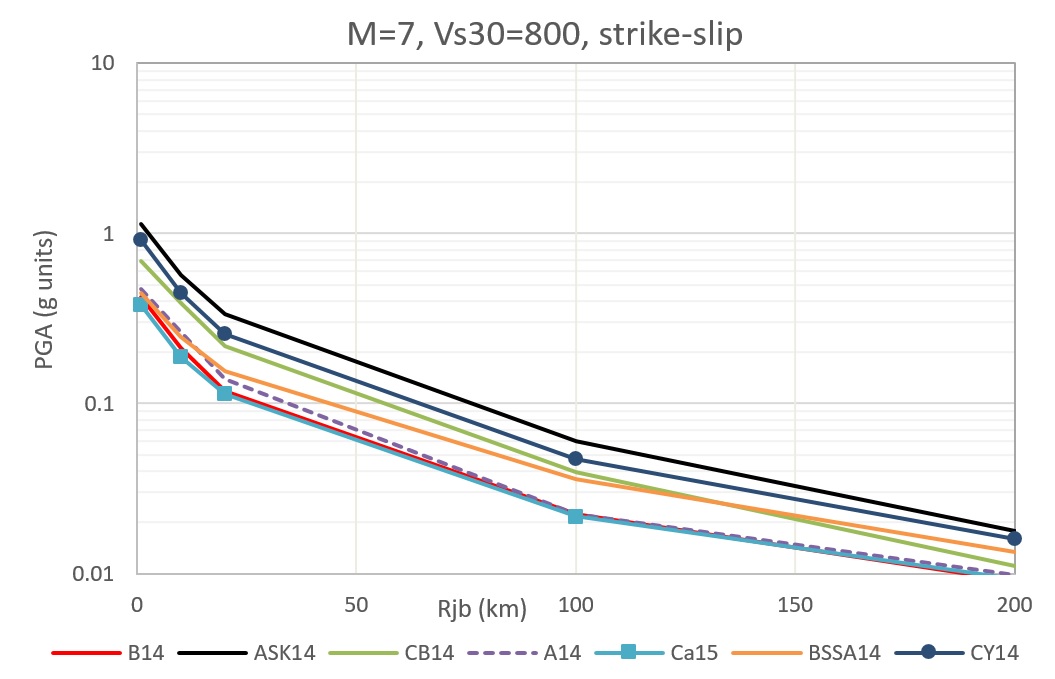
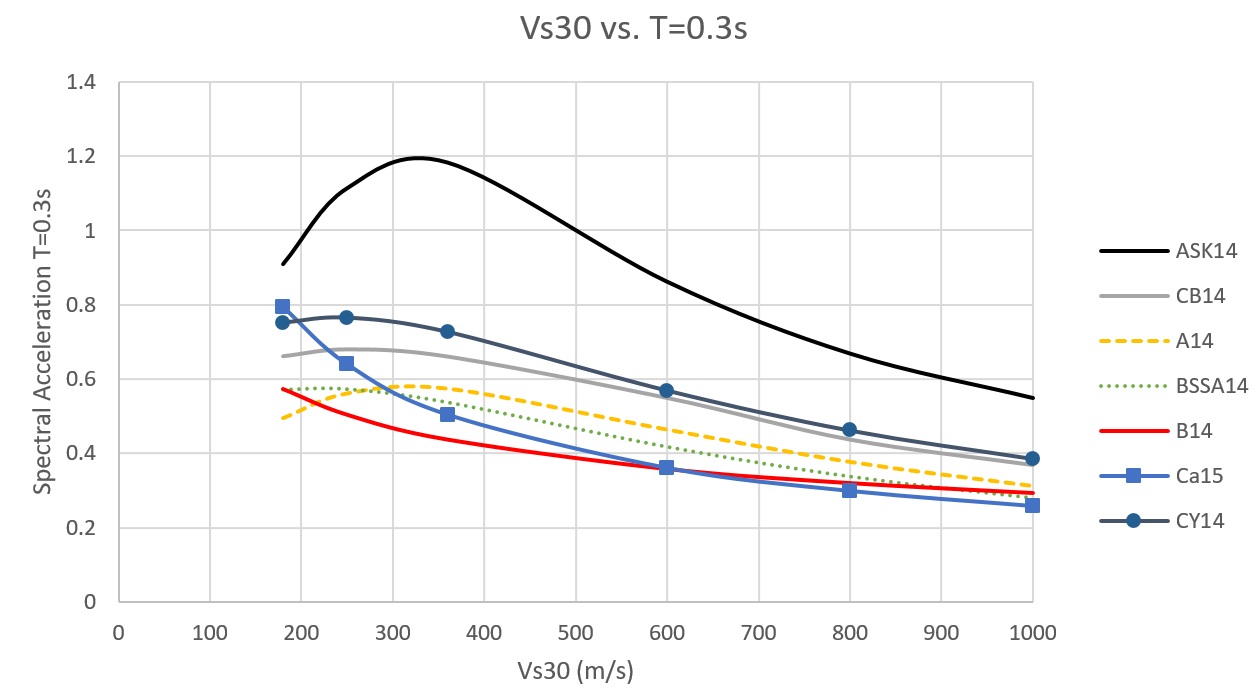
5️⃣ Ground Motion Prediction Model (GMPEs)
GMPEs predict strong ground motion based on earthquake source, path, and local site conditions.
Four basic types:
-
Shallow crustal – active region
-
Shallow crustal – stable region
-
Intermediate-depth (intraslab) earthquakes
-
Subduction interface earthquakes
ADC Ltd. tests candidate GMPEs against historical earthquakes to select the project-specific suite with appropriate weights for logic tree analysis.
6️⃣ Software 💻
We use OpenQuake Engine, an open-source tool for seismic hazard and risk assessment.
-
Transparent, reproducible, community-supported.
-
Written in Python with scientific libraries for robust modeling.
7️⃣ Presentation of Results 📈
PSHA outputs can include:
-
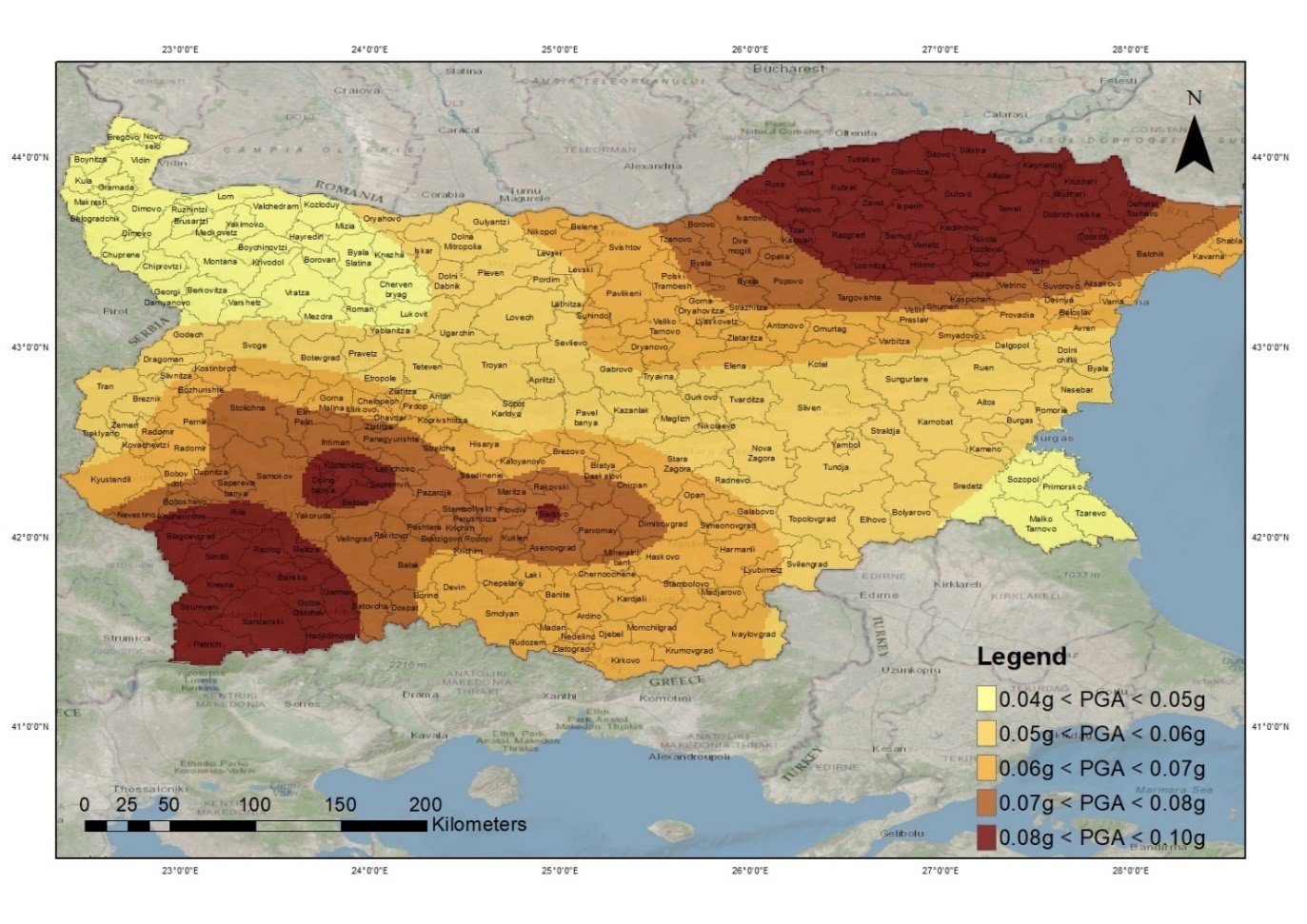
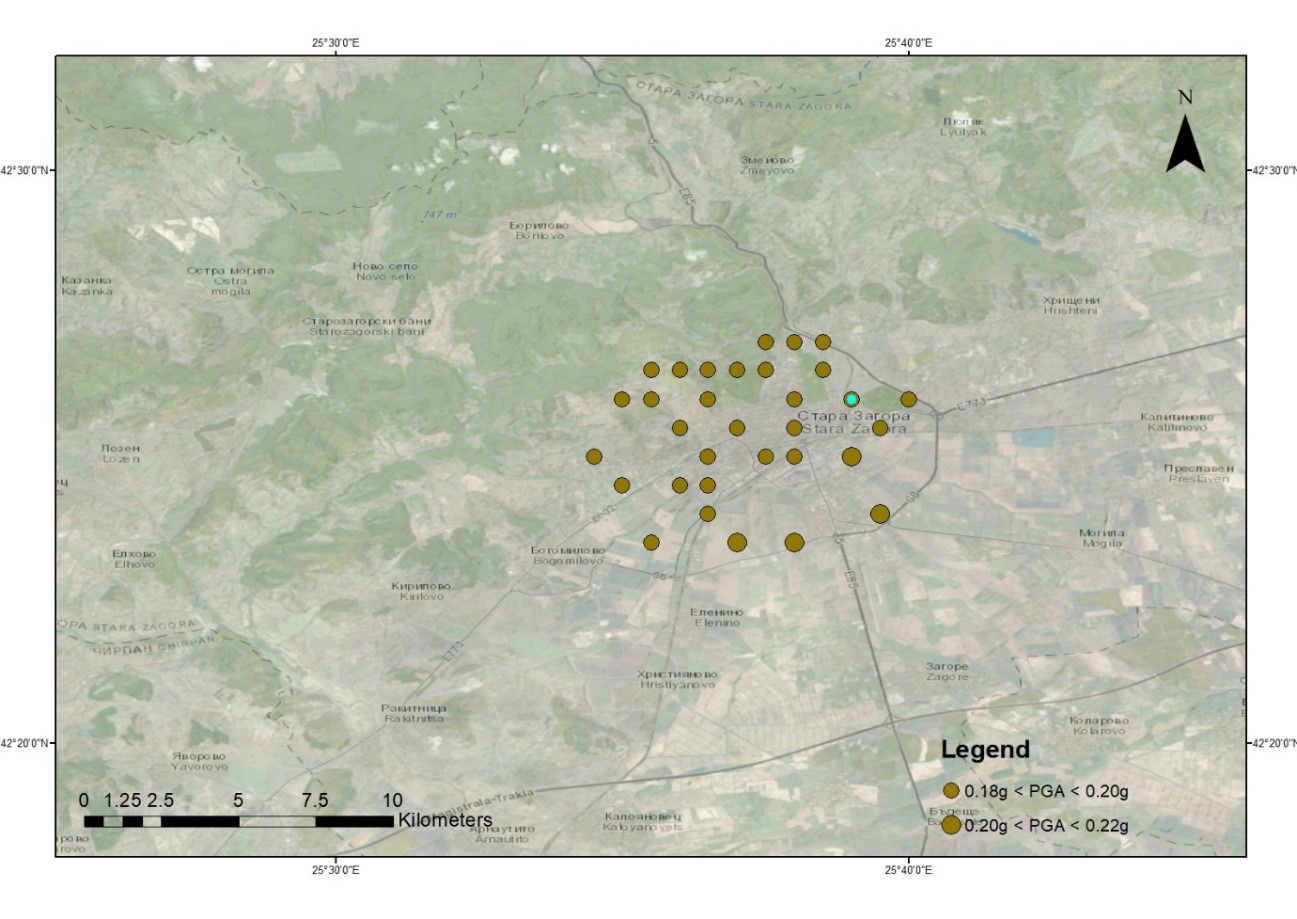
Seismic hazard maps
-
Seismic hazard curves
-
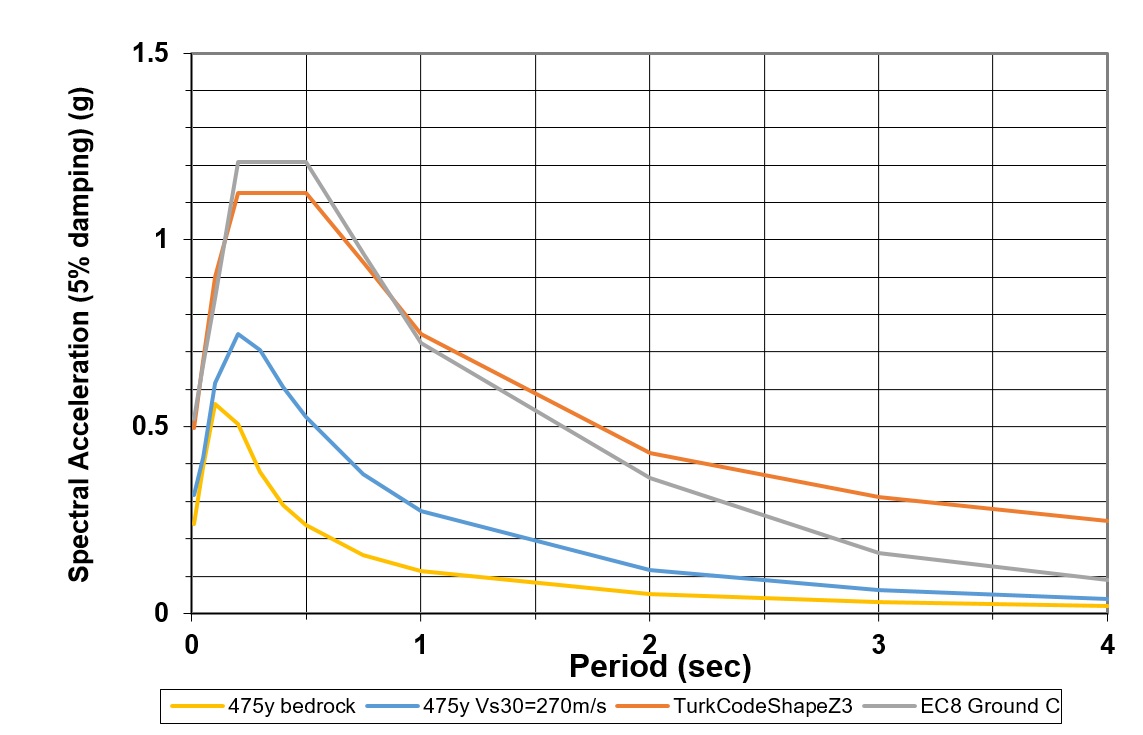
Uniform Hazard Spectra (UHS) or EC8 design spectra
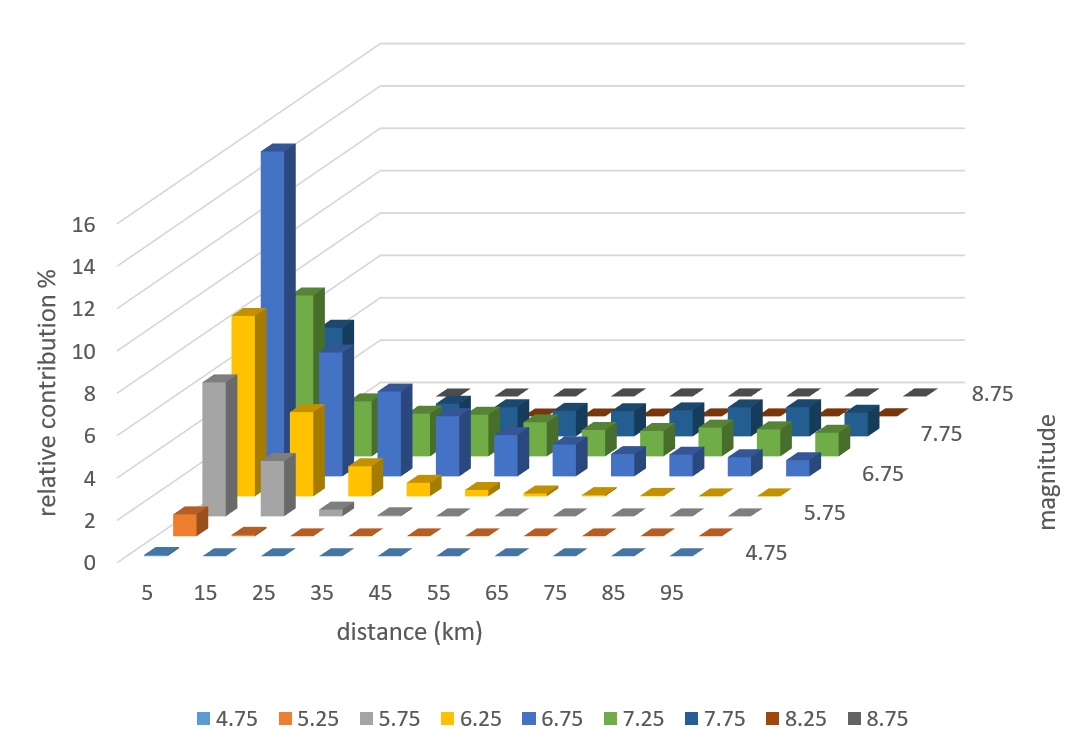
8️⃣ Deaggregation of the PSHA 🔍
Deaggregation identifies which earthquake magnitudes and distances contribute most to the hazard.
-
Displayed as histograms for easy interpretation.
-
Modes of distribution highlight the earthquakes that dominate site hazard.
9️⃣Nuclear & Industrial Site Evaluation 🏗️
We support project owners and investors in selecting and evaluating sites for critical infrastructure, including:
-
Nuclear power plants – full siting assessments according to IAEA and EPRI guidelines.
-
Hydrocarbon pipelines & industrial facilities – geotechnical and seismic risk evaluation.
-
Regulatory compliance support – ensuring alignment with national and international safety frameworks.
Our approach includes:
-
Regional screening – identify potential zones using geophysical, geological, and seismological data.
-
Site-specific characterization – detailed investigation of soil, rock, and seismic conditions.
-
Hazard integration – combining PSHA results with geotechnical, hydrological, and environmental data.
-
Design basis definition – providing realistic and defensible ground motion and hazard inputs for infrastructure design.
By integrating PSHA with robust site evaluation, we provide practical, reliable, and defensible recommendations for site selection and risk-informed decision-making.
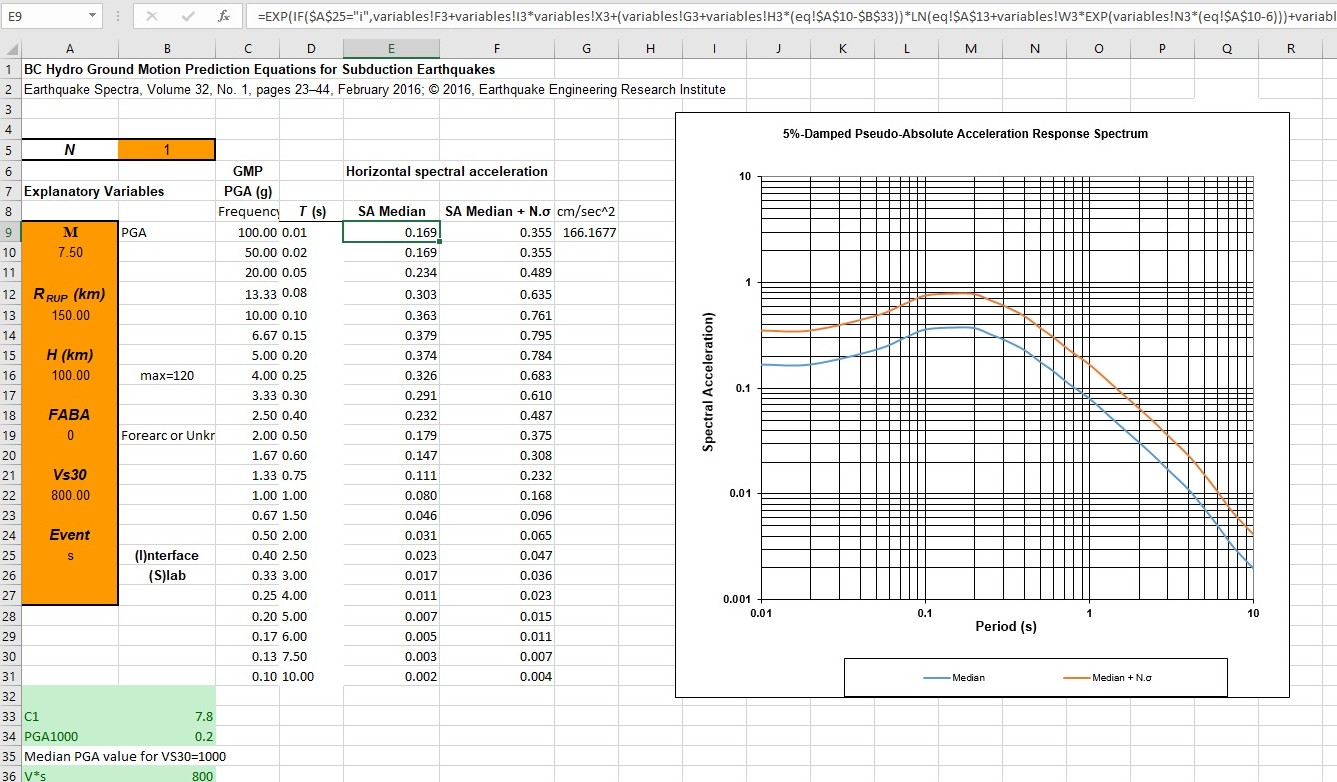
Seismic Hazard Curves
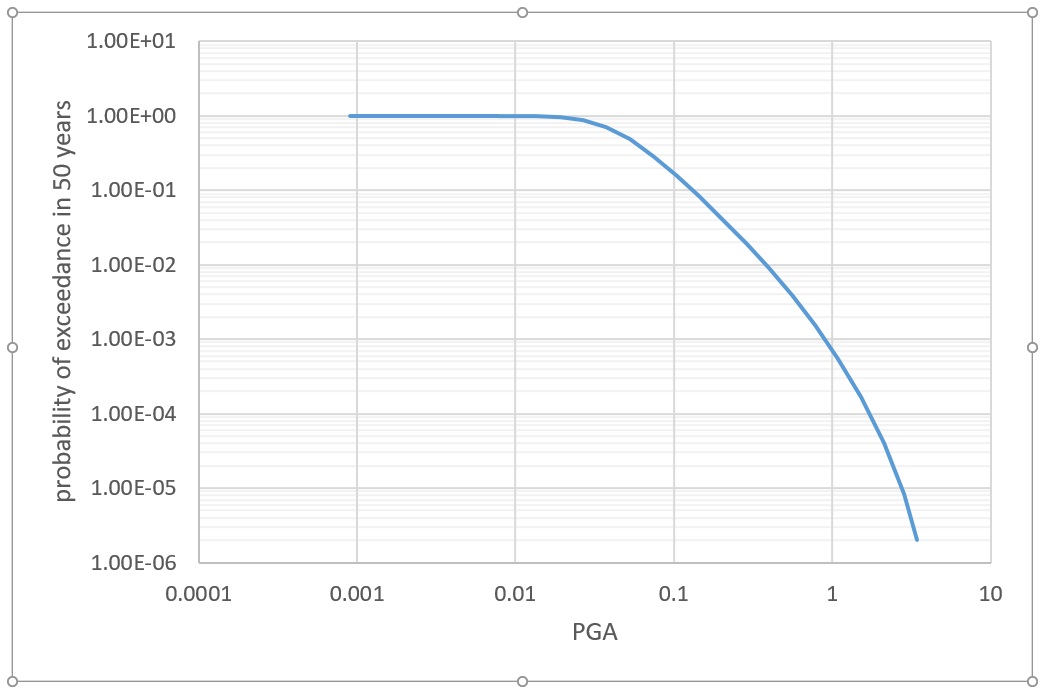
And Uniform Hazard Spectrum and or design EC8 standard shape spectrum